Everyone should know these facts about a vegan diet including information on B12, Iron, Calcium, sustainability and seaweed. Information on vegan nutrition and dispelling common criticisms.

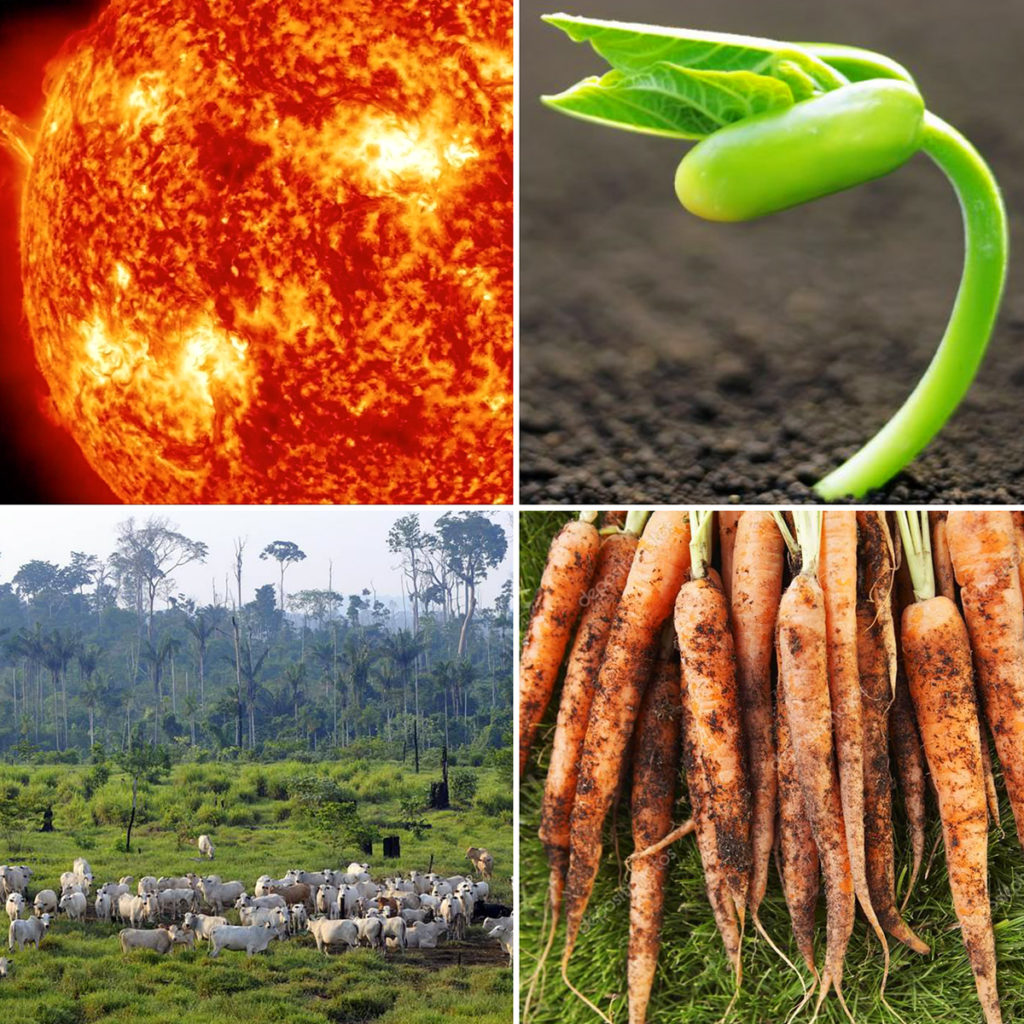
Eat homegrown or organic carrots with some dirt and microbes to get b12.
Wash off the dirt at home and the carrots will still contain B12.
Avoid the pressure washed veg in supermarkets as all the b12 and other beneficial microbes have been washed away.
This was proven by a study that found family members eating exactly the same vegan diet
Those eating supermarket washed produce were lacking in B12, those eating non pre-washed veg had optimum B12 levels.

Expose skin for a short time to get vitamin D, but never get burnt.
Even in the winter, you can still get vitamin D.
Mushrooms can be left in the sunlight to create a plant source of vitamin D.
Many people both vegan and carnivore are lacking in vitamin D.
However vitamin D supplements are cheap and effective.

Leafy greens, almonds, figs, beans, sesame seeds all contain a good amount of calcium.
Incorporating a few high calcium plant based foods makes it easy to get your RDA of calcium.
Try having some tahini on your evening meal or my vegan calcium fudge recipe.

All essential amino acids can be found in plant foods.
Just eat a variety of plant foods to get all of your amino acids.

High in plant protein with a very low impact on the environment.
Grow virtually anywhere and add nutrients to the soil as they grow.
Above is my recipe for oil free lentil chips.

Plant foods like chia seeds, walnuts and flax seeds all contain these fatty acids.
Check out my recipe for overnight chia puddings.

With a bit of knowledge, it’s easy to be vegan and be lacking in nothing.

A small amount of seaweed goes a long way.
Great source of iodine – 1g of kelp can contain 15 times the RDA.
Enhances the flavour of food and a great source of plant nutrition.

Chickpeas, lentils, sesame, molasses, potatoes, tomatoes, greens, lima beans, quinoa all contain a decent amount of iron.
Combine high iron foods with vitamin C like kiwi, oranges, broccoli for great iron absorption.

Choose simple whole food stables (fruit, veg, legumes) and prepare from scratch for an inexpensive very healthy diet.

The meat and dairy industry has a far greater impact than all transport and manufacturing combined.
Even if you can’t go vegan, just eating more vegan meals make a huge difference.
Vegan and plant based are two different things. Vegan is a lifestyle and plant based is a diet. More information on the difference between vegan and plant based.

Love your work and your dedication. Thank you.
Thanks so much, glad you liked this post Fiona – I thought it would be some interesting points to share on a vegan diet and nutrition
what kind of blender are you using for your recipes???
Usually a bullet or a ninja. I pop a link below many recipes to it 🙂